(2) Practical guide-memristor
Brain-inspired experiments-STDP
What is the difference between a presynaptic neuron and a postsynaptic neuron?
Anatomically, the presynaptic neuron is the neuron before the synapse, this neuron is delivering the nervous "message" across the synapse to the postsynaptic neuron. Thus, the difference is just of the location. One sends the chemical message (neurotransmitters) and the other one receives it.
Spike-timing-dependent plasticity (STDP) is the ability of natural or artificial synapses to change their strength according to the precise timing of individual pre- and/or post-synaptic spikes.
How we can perfrom STDP test for a memristor device?
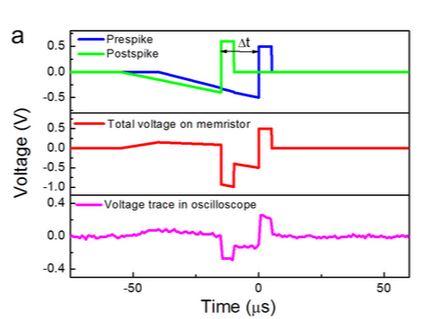
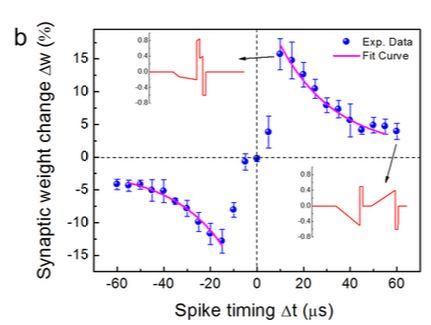
STDP implementation. (a) Pulse schemes used to implement STDP. The upper part shows a pair of pre- and postspikes with a 25-μs negative temporal difference. The middle shows the total effective voltage on the memristor, which is Vpre(t) − Vpost(t). The lower part shows the voltage trace captured by an oscilloscope. (b) The asymmetric Hebbian learning STDP rule of memristor. The synaptic weight changes are plotted as a function of the time difference between the presynaptic spikes and postsynaptic spikes. The percentage changes are calculated with respect to the same initial value for all Δt, and the maximum change is approximately 15%. The error bars represent one standard deviation obtained from four measurements. The insets show two effective voltage pulses for Δt = 10 μs and 60 μs, respectively.
Ref.DOI: 10.1038/srep04906