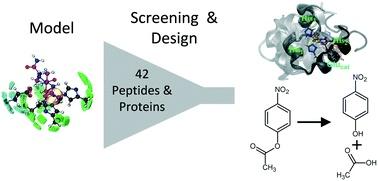
New paper about metallopeptides & computational design approach
Hydrolytic zinc enzymes are common targets for protein design but the computational design of metal-containing proteins remains challenging due to the need to properly model protein–metal interactions. To overcome these limitations, the authors propose to integrate information of protein–metal interactions in long time scale simulations by focusing on the inherent flexibility of small proteins and their interactions with the metal ion by molecular dynamics simulations and spectroscopic studies.
Our last paper, from Henrique Carvalho, Ricardo Branco, Fábio Leite and Cecília Roque, in collaboration with colleagues from ITQB (Manolis Matzapetakis) and CNRS (Olga Iranzo) is now published in Catalysis Science & Technology.
Find more about "Hydrolytic zinc metallopeptides using a computational multi-state design approach" here: https://rsc.li/3519xg3