Electronic control of drug release from gauze or cellulose acetate fibres for dermal applications
- Citation:
- Baptista, Ana Catarina, Miguel Brito, Ana Marques, and Isabel Ferreira. "Electronic control of drug release from gauze or cellulose acetate fibres for dermal applications." Journal of Materials Chemistry B 9 (2021): 3515-3522.
Abstract:
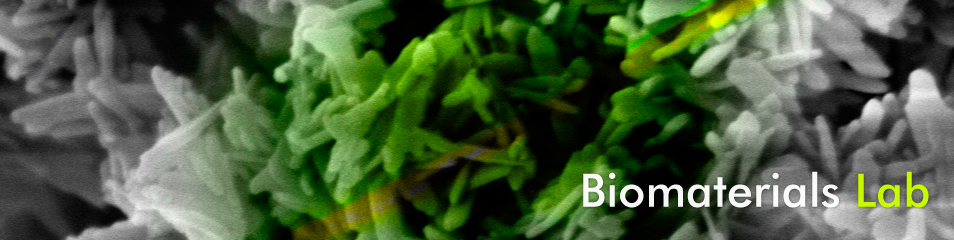
Electronic controlled drug release from fibres was studied using ibuprofen as a model drug, one of the most popular analgesics, to impregnate gauze and cellulose acetate (CA) membranes. Conductivity in the range of 1–10 mS cm−1 was obtained in polypyrrole (Ppy) functionalised gauze and CA fibres, providing voltage-controlled drug release in a system consisting of Ppy/Ibuprofen/Ppy membranes and an Ag electrode. SEM images evidenced the Ppy adhesion to fibres and Micro Raman spectra proved drug incorporation and release. A small wound adhesive built with these membranes retains ibuprofen at 1.5 V and quickly releases it when −0.5 V is applied.