RailScan
Rail corrugation is a problem extensively felt by railway companies. This phenomenon appears in the railhead by the form of ondulations.
There are two types:


- Short wavelength rail corrugation (3-10 cm)
- Long wavelength rail corrugation (10-100 cm)
- Dynamical mechanical interaction of the vehicle-track system as wear and various forces.
- Noise makes travel uncomfortable for passengers.
- Vibration reduces the rail and wheel lifetime.
- If not early detected, and treated (grinding), the problems aggravate, and becomes more and more expensive treat the problem.
-
Axle-box or vehicle Accelerometer data
- Classical Spectral Analysis
- One Third Octave Filter power representations
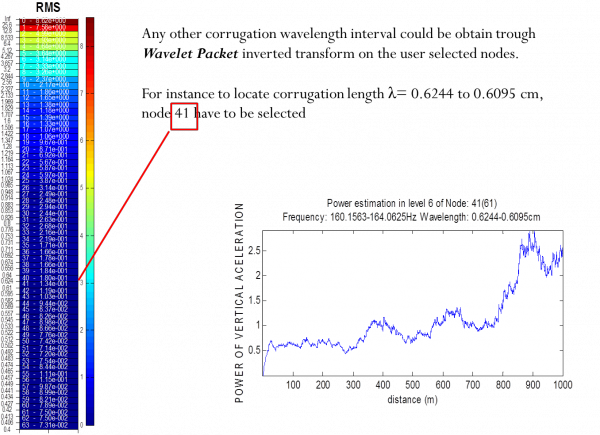
- Time-scale representation with user selected wavelets Wavelet-Packet implementation that results in power spectrum in the corrugation
- Wavelengths
- Rail corrugation localization in the rail and its signal recovering in selected wavelet nodes
- Wavelet analysis generally outperforms the classical spectral methods for non-stationary signals such as the rail corrugation data, namely in data affected by noise.
- In recent times Wavelet analysis has been successfully applied to similar signals, and seems to be the adequate tool for these signals. However there is a great deal of research work in order to validate these methods.